Factors Affecting UV LED Performance
The principle of LED light emission is that electrons (n) and holes (p) emit photons (photon) when they combine at the semiconductor interface to emit light. The main factors affecting the luminous efficiency of LEDs are: chip structure, chip surface roughness, LED package structure, encapsulation material, and optical design.
The following discussions are focusing on the optical part of LED package:
Encapsulation lens material
Nowadays, the chip technology of UVA LED has matured, and chips with high current input such as 700 mA, 1 A and even more have been successfully commercialized in mass production. Under the condition of this input current, a large amount of heat and highly destructive ultraviolet rays will be generated. Energy, if the lens material cannot withstand it, it will rapidly age, fog, turn yellow, and even burn, so the selection of optical encapsulation material becomes very important.
Most of the early UV LED lens materials were made of silicone by direct molding. The silicone material was responsible for the three tasks of refractive index matching, material bonding, and optical structure of the package. In the current UV LED packaging structure, silicone can only be used for the bonding of lenses and substrates, reducing the scope and time of direct ultraviolet radiation. Whether it is UVA or UVC, the reliability of all silicone packaging is not enough.
Silicone is a polymer material, and the double bond structure in the polymer chain cannot withstand the material damage caused by high intensity ultraviolet rays . The specific characteristics of the aging of the lens are: the lens surface is fogged , and the color changes from transparent to yellow or even burnt black .
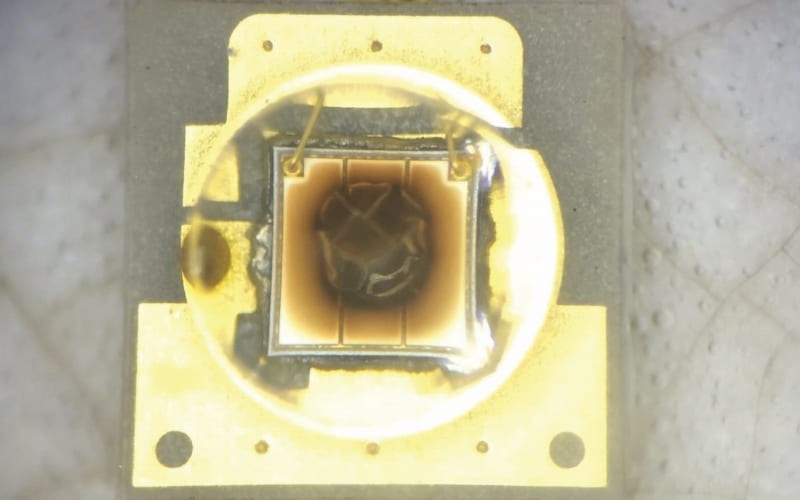
The traditional silicone package lens material can no longer meet the reliability requirements of high-current chips
NOVAXIL™ Silica Lenses
The UVA transmittance of standard NOVAXIL™ silica lenses can reach 92 % when uncoated, and the transmittance of ultra-high-purity UVC grades at 260 – 280 nm can reach more than 90 %, because the material itself does not absorb UV at all Spectrum, NOVAXIL™ Silica Lenses can withstand high-intensity UV light for a long time without aging, embrittlement, yellowing, etc., so NOVAXIL™ Silica Lenses have become the preferred lens material in UV LED packaging.
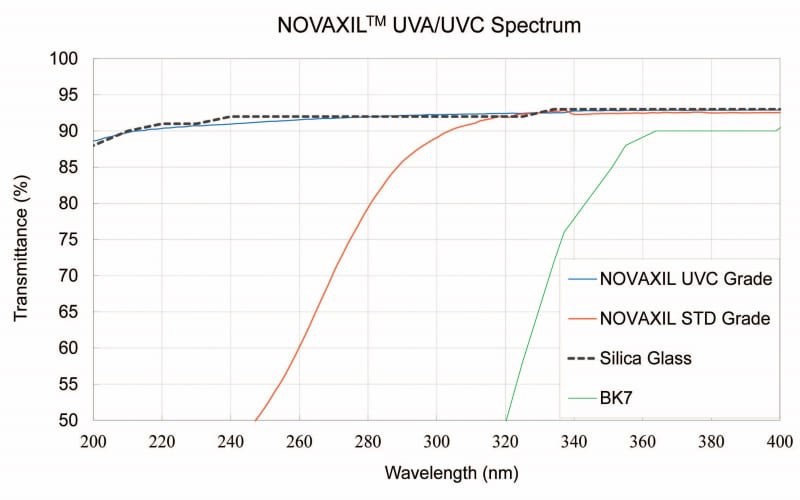
NOVAXIL™ silica glass has excellent transmittance in UV (200 – 400 nm)
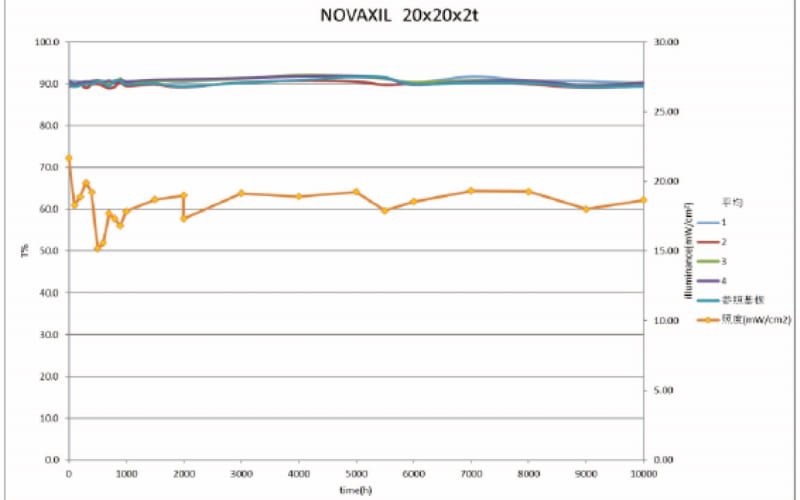
NOVAXIL™ Silica Lenses can withstand 10,000 hours of continuous exposure to UV mercury lamps at the dominant wavelength of 253.7 nm without any degradation
Lens Optical Structure
Optical structure is another important pillar that affects the efficiency of LED package, and the optical structure on LED package is often called primary optics. A good primary optical design can effectively guide the light in the package. With the curved surface design of the primary optical lens, the large-angle stray light emitted by the chip can be extracted and shaped, which reduces the total reflection effect inside the package and improves the package body. Light extraction efficiency.
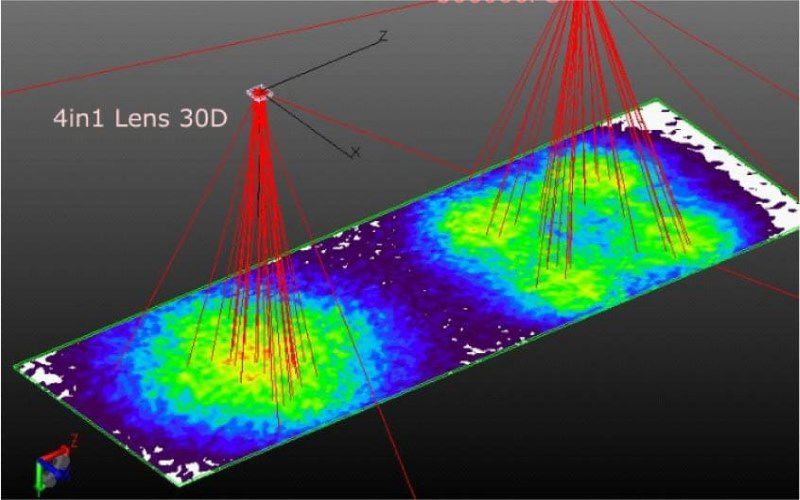
Another main purpose of the lens package is to adjust the angle. The most direct benefit of converging the angle is the improvement of the illuminance. Compared with the flat package, the package body with the lens can easily double the center illuminance by one optical operation. For the application of UV transmission, especially in integrated array applications such as exposure, curing, sterilization, etc., the encapsulated lens can indeed maintain high-intensity UV illumination while transmitting at a long distance, thereby meeting the needs of the application.
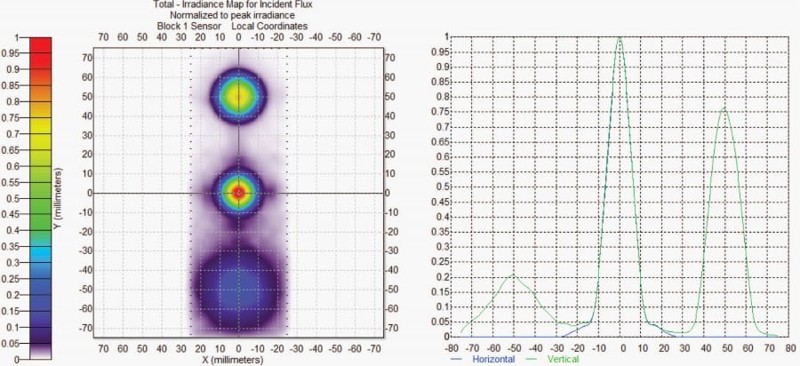
According to different application requirements, select the appropriate primary optical light angle as the basis for UV LED module design